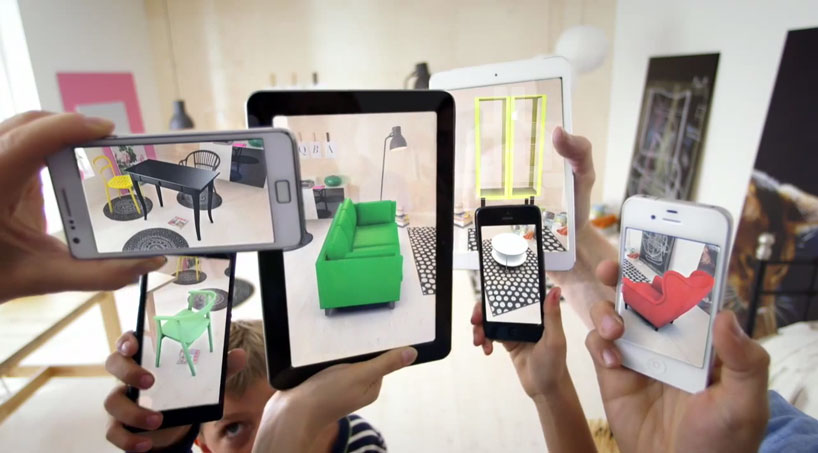
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are technological innovations that have the power to reshape our interaction with the world and each other. While they may seem similar on the surface, each offers distinct experiences and benefits. This article aims to dissect the key differences between AR and VR, explore their diverse applications, and delve into the technology that powers them. We’ll also examine the ethical considerations and speculate about the future of these groundbreaking technologies.
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality (AR) is a cutting-edge technology that seamlessly merges digital elements with the physical world. By employing computer-generated imagery, AR enriches your experience of reality. It doesn’t replace the world around you but amplifies it by superimposing relevant information, interactive features, or even whimsical characters from your favourite video game.
Real-World Example: Surgery Aid
For instance, AR is making waves in the medical field, particularly in surgery. Surgeons now use AR headsets that overlay critical information, such as real-time MRI scans, directly onto the patient’s body during procedures. This augmentation assists surgeons in making precise incisions and thus reduces the risk of errors. A study published in the Annals of Surgery demonstrated that AR-assisted surgeries reduced the time needed for certain procedures by up to 10%, improving efficiency and outcomes (Annals of Surgery).
What is Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality (VR), in contrast to AR, fully immerses you in a digitally created three-dimensional environment. Donning a VR headset can transport you from your living room to a recreated historical Rome or to the depths of an ocean teeming with coral reefs. This total immersion has applications that extend far beyond mere entertainment.
Real-World Example: Treating PTSD
In the field of psychology, VR is being employed as a therapeutic tool for treating Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Through carefully crafted simulations, patients are gradually exposed to triggers in a controlled environment, allowing them to better manage their symptoms. Clinical studies, such as those published in The Journal of Anxiety Disorders, have shown that VR-based exposure therapy is as effective as traditional methods, opening the door for wider application of this technology in mental health treatment (Journal of Anxiety Disorders).
Key Differences Between AR and VR
While both AR and VR offer immersive experiences, they diverge significantly in their approach and impact.
| Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) | |
|---|---|---|
| User Experience | Adds digital elements to a live view, typically through a smartphone or AR glasses. | Provides a fully immersive environment where the user is cut off from the real world. |
| Hardware Requirements | Accessible on devices people already own like smartphones and tablets. | Requires specialized hardware like VR headsets and motion controllers. |
| Interactivity | Allows interaction with both digital and physical elements. | Interaction is limited to the digital world but offers deeper immersion. |
| Versatility | Can be flexibly integrated into daily life. | Generally more enclosed and event-based. |
| Realism vs. Fantasy | Enhances the real world, making it more informative or entertaining. | Transports you to entirely new, fantastical worlds, offering an escape from reality. |
Applications in Various Industries
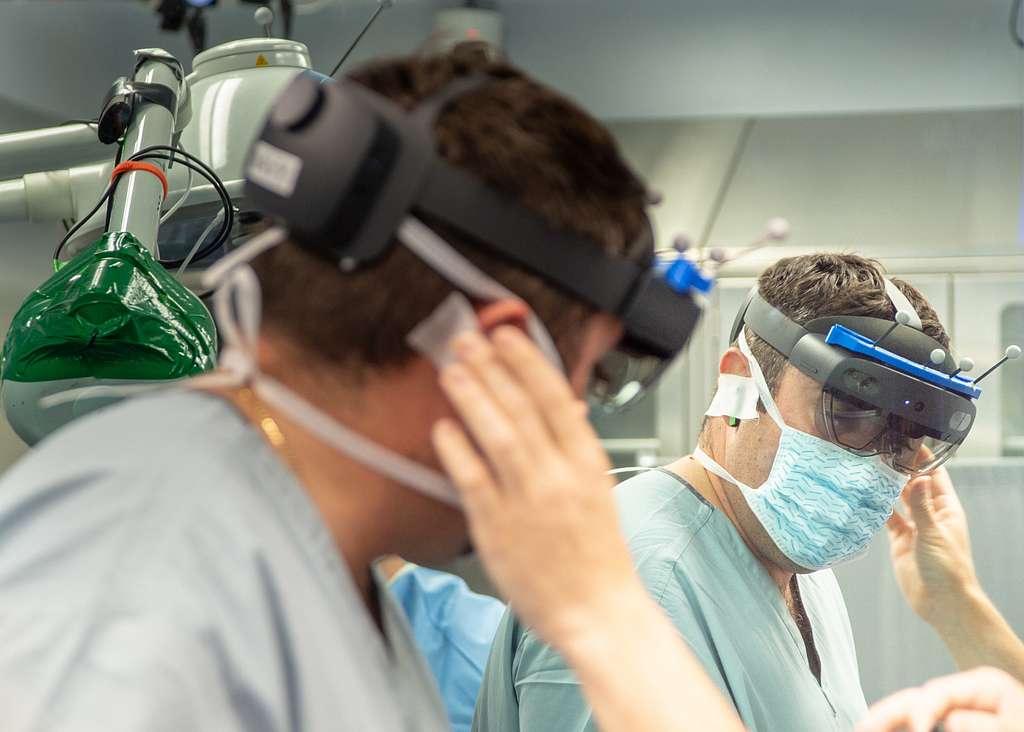
Augmented Reality
- Healthcare: AR is proving to be a lifesaver in healthcare. Surgeons are using AR-enabled goggles to overlay critical information onto their field of view during complex procedures. According to a study published in the Journal of Medical Systems, AR-assisted surgery led to a 10% reduction in operation time and improved surgical precision [Journal of Medical Systems, 2018].
- Retail: Virtual fitting rooms and interactive 3D ads are not just buzzwords but are significantly changing the consumer experience. For example, Lacoste’s AR app has reported a 30% increase in customer engagement since its launch, showing how interactive shopping can directly influence sales [Retail Dive, 2020].
- Education: The traditional textbook is getting a digital makeover thanks to AR. The University of California reported that students who used AR-powered educational tools scored 27.4% higher in retention tests compared to those using traditional methods [University of California Study, 2019].
Virtual Reality
- Training & Simulation: Companies like Boeing and Walmart are employing VR for employee training. Walmart, for instance, trained over 1 million employees using VR and found a 10-15% increase in retention rates compared to traditional training methods [Harvard Business Review, 2020].
- Tourism: VR tourism isn’t just a pipe dream; it’s happening. Major travel companies like Expedia are offering virtual tours of destinations, and according to their data, such experiences have led to a 15% increase in actual bookings [Expedia Report, 2021].
- Mental Health: The use of VR in treating mental health issues like PTSD is gaining traction. A study in the Journal of Traumatic Stress found that patients undergoing VR-based exposure therapy showed a 45% reduction in PTSD symptoms compared to traditional treatments [Journal of Traumatic Stress, 2017].
Technological Foundations
Both AR and VR rely on sophisticated technologies to deliver their unique experiences.
- AR: Utilizes sensors, cameras, and sometimes even machine learning algorithms to integrate digital information with the real world.
- VR: Employs high-definition displays, motion trackers, and haptic feedback systems to create a convincing alternate reality.
Though distinct, these technologies share components like accelerometers and gyroscopes for tracking movement, and powerful computing capabilities to render high-quality graphics.
Future Outlook of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are two of the most exciting new technologies to emerge in recent years. Both technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with the world around us, and their development is accelerating rapidly.
Augmented Reality
AR overlays digital information on the real world, such as directions, labels, or even creatures from a video game. It is becoming increasingly popular, with applications in gaming, education, and even healthcare. For example, AR can be used to provide real-time translations of signs or to help students learn about anatomy.
Recent advances in AR technology have made it more affordable and accessible than ever before. This, combined with the growing popularity of smartphones and other mobile devices, is expected to drive the growth of AR in the coming years.
Virtual Reality
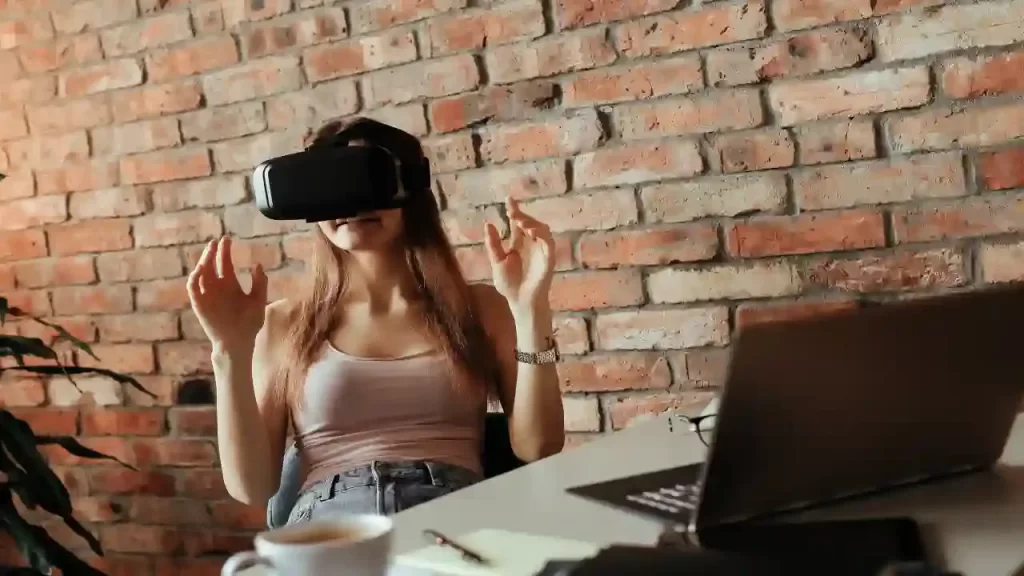

VR creates a simulated environment that a user can interact with. VR headsets are used to create the illusion of being in a different place, such as a video game world or a different city. VR is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to be used for a variety of applications, such as gaming, training, and even therapy. For example, VR can be used to train surgeons or to help people with anxiety disorders.
The development of VR is also being accelerated by advances in technology, such as the development of more powerful graphics processors and the use of eye-tracking technology to improve immersion.
Converging Paths
AR and VR are often seen as two distinct technologies, but they are increasingly converging. Future hybrid systems could combine features of both AR and VR, offering experiences that are both rooted in reality and expansively imaginative. Such a blend could disrupt industries ranging from healthcare and education to retail and entertainment.
Societal Implications
AI’s influence on society is twofold: it promises transformative benefits like medical breakthroughs and climate solutions, but also poses risks such as job loss and bias in decision-making. Its ethical implementation is crucial for maximizing benefits while minimizing harm.
Ethical Considerations
Legislation is increasingly catching up to the rapid developments in AI. In the U.S., for instance, the Algorithmic Accountability Act of 2019 aimed to hold companies accountable for biased algorithms. Similarly, the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has articles that touch on automated decision-making. Currently, there is active discussion around the AI in Government Act, which aims to establish guidelines for federal use of AI.
Europe is also looking at even more stringent rules with its proposed Artificial Intelligence Act, focusing on high-risk AI systems. Such legislations aim to address issues like transparency, discrimination, and data privacy. Following these rules and actively engaging in discussions about new policies is essential for the ethical development and deployment of AI.

Data Privacy and Security
AR and VR applications often require access to sensitive personal data, including location, eye movement, and biometrics. This raises questions about data privacy and security. Legislators are already grappling with these issues, and bills like the Consumer Online Privacy Rights Act in the U.S. have been proposed to protect consumers. However, the fast pace of technological advancements often outstrips the legislative process.
Accessibility
The cost of AR and VR hardware can be a limiting factor for widespread adoption. While prices are falling, these technologies still remain largely inaccessible to underprivileged communities. The digital divide could widen, reinforcing existing societal inequalities.
Surveillance and Ethical Use
AR can be used for surveillance purposes, offering unprecedented tools for monitoring public and private spaces. This has raised ethical debates on the balance between security and personal freedom. Concerns are amplified by the use of facial recognition technologies, a subject under scrutiny in many jurisdictions worldwide.
Psychological Effects
The immersive nature of VR has the potential for both positive and negative psychological effects. On the positive side, it’s being used for treating conditions like PTSD; however, questions around potential addiction, desensitization, or exacerbation of mental health conditions remain open subjects of study.
Ethical Frameworks and Legislation
Given the rapidly evolving landscape, ethical frameworks for AR and VR are in a nascent stage. Researchers and ethicists are calling for technology-specific guidelines that address these ethical quandaries. For instance, The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has already started to work on standards for “Ethically Aligned Design” of autonomous systems, which could be applied to AR and VR.
Environmental Concerns
The manufacturing and usage of AR and VR hardware also have environmental impacts, including the use of non-renewable materials and energy consumption. As the popularity of these technologies increases, their environmental footprint could become a significant concern.
Summary of the future

AR and VR are two exciting new technologies with the potential to change the world. The future of these technologies is bright, and it will be interesting to see how they are used in the years to come.
AR and VR are becoming more affordable and accessible. This is due to the development of new technologies, such as lightweight and affordable AR headsets.
AR and VR are being used in a wider range of applications. These include gaming, education, healthcare, training, and entertainment.
The development of AR and VR is being accelerated by research and investment. Major technology companies, such as Google, Facebook, and Microsoft, are investing heavily in AR and VR research and development.
The societal implications of AR and VR are still being debated. There are concerns about the potential for these technologies to be used for surveillance, addiction, and other negative purposes.
Overall, the future of AR and VR is bright. These technologies have the potential to change the way we interact with the world around us, and they are being used in a wider range of applications. However, it is important to be aware of the ethical implications of these technologies and to use them responsibly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between AR and VR?
AR (Augmented Reality) overlays digital elements onto the real world, enhancing our perception and interaction with it. VR (Virtual Reality), on the other hand, provides an entirely immersive experience in a digitally generated environment.
Can AR and VR co-exist?
Yes, in fact, experts predict that these two technologies will increasingly converge in the future, offering hybrid systems that combine the best features of both.
Are there any health risks associated with using AR and VR?
Prolonged use of VR can lead to motion sickness or eye strain. AR, if not used responsibly, could potentially distract users and cause accidents.
Further Reading and Resources
For those who are keen to dive deeper into the fascinating world of AR and VR, here are some resources to explore:
Books:
“Infinite Reality: The Hidden Blueprint of Our Virtual Lives” by Jim Blascovich (Author), Jeremy Bailenson (Author)
“Augmented Human” by Helen Papagiannis
Websites and Blogs:
Research Papers:
“A Review of Research on Augmented Reality in Education: Advantages and Applications” – Canadian Center of Science and Education
“How virtual reality has changed out lives” – College of Engineering and Computer Science, University of Michigan-Dearborn
Looking to Buy a VR headset?
Try the Meta Quest 2 available on Amazon
Conclusion
In our exploration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), we’ve seen how these technologies are far more than trendy buzzwords. They’re fundamentally altering our interactions with both the digital and physical worlds, offering boundless opportunities across sectors like education, healthcare, and entertainment. While the integration of AI into AR and VR presents exciting future prospects, ethical challenges like data privacy and potential misuse must not be overlooked. As these technologies continue to mature, we can anticipate not just transformative changes in specific industries but a revolutionary impact on our daily lives. As we stand on the cusp of this digital paradigm shift, an open mind and a critical eye are essential for navigating both the opportunities and responsibilities ahead.
This concludes our in-depth look at AR and VR, technologies that are not only shaping our immediate future but also challenging our very understanding of reality.
Thank you for embarking on this journey with us; we anticipate many more explorations into groundbreaking technologies ahead but in the mean time why not take the plunge into VR as avid users of the oculus quest we highly recommend it!